Polar station im. Dobrovolsky station will be rebuilt. Australians will help
Polar station im. Dobrowolski station will be rebuilt. Australians will help
The polar station named after Antoni Dobrowolski at Bunger Oasis, which has been unused for nearly 40 years, will be in use again. The Polish Academy of Sciences and the Institute of Geophysics of the Polish Academy of Sciences have announced the signing of an agreement with Geoscience Australia, under which scientists from both countries will conduct joint research in the Antarctic area.
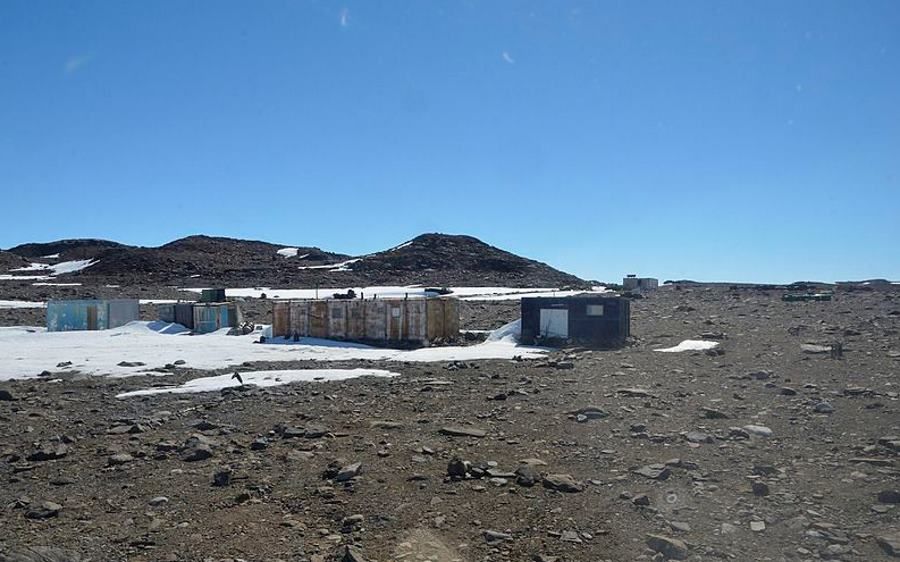
For years, the defunct Polish polar station im. Dobrowolski is located in East Antarctica, in the Bunger Oasis. The research station at the site was established by the Russians in 1956. Woat the time it was called „Oasis”. The inland base is difficult to get to, which is why Soviet scientists only used the station for two years. In 1959 the station was handed over to Poland and during the first Polish scientific expedition to Antarctica it was named in honor of geophysicist, polar explorer and educator Antoni Boleslaw Dobrowolski (1872-1954).
The polar station consists of m.in. two wooden houses – „Warsaw” i „Krakow”. There are also smaller pavilions and an airstrip located 15 kilometers awayoin from the buildings. The latest research expedition to the im. Dobrowolski took place in 1979 and since then the station has not been by Polish polar explorersoin use. However, Russians and Australians occasionally look there. The latter, in 1986, opened the Edgeworth David Base summer polar station just over 7 kilometersoin from the Polish station. The polar station of im. Dobrowolski Island is currently managed by the Institute of Geophysics of the Polish Academy of Sciences.
But Poland has two polar stations in Antarctica. In addition to the stations, im. We also have the Dobrowolski station, which has been in continuous operation since 1977, and the. Henryka Arctowskiego located on the Island of Krola George in the Shetland archipelagooin the Southern. The station im. Arctowski station raised nearly 90 million in Novemberoin PLN from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education. Funds are to be used for reconstruction of the station’s infrastructure. Read more about it in the text: 88 millionoin gold for the Polish Antarctic Station im. H. Arctowski.
Revitalization also awaits the im station. Dobrowolski. The Polish Academy of Sciences and the Institute of Geophysics of the Polish Academy of Sciences have concluded an agreement with Geoscience Australia – Statement of Cooperation in Antarctic Geoscience. Under the document, scientists from both countriesoIn addition to the autonomous geophysical stations, they can carry out jointolne earth science research in the Antarctic area. This is the first such document concluded between Poland and Australia, and the first stage of wspohe work is about to revitalize the abandoned station.
„The signed document is the basis for the cooperationolarly scientific activities in accordance with the Australian Antarctic Strategic Science Plan and the Polish Polar Research Strategy. Elements of wspohe cooperation will be the exchange of scientific and technical ideas and the exchange of information and scientific data for the development of research at sea and on the Antarctic continent. The first stage of the cooperation will be the revitalization of the Polish im polar station, which has not been used for more than 40 years. Antoni B. Dobrovolsky, located in the Bunger Oasis. The station will become a lynchpin ofołk to erect autonomous geophysical stations on the exposed rocks of the Antarctic continent. The first expedition of Polish geophysicists after 40 yearsow to Bunger Oasis is planned in three to four years, using the modern Australian icebreaker Nuyina” – We read on the website of the Polish Academy of Sciences.
Polar station im. Dobrowolski was built on rocks, not on the ice sheet. It lies on the shore of Figure Lake. Bunger Oasis is a środcontinental, ice-free archipelago among theod fresh- and saltwater lakes. The first historically recorded human contact with the oasis took place in 1947. The aircraft commanded by Col. David Bunger landed on one of the lakes of the archipelago, later named Bunger Hills.
The station’s unique location allows it to conduct the entire spectrum of natural and technical research. Some of these studies (seismology, geomagnetism, meteorology, atmospheric physics) will be carried out continuously, using autonomous measuring stations, while environmental studies will be carried out during the summer seasons (seasonal studies), as part of subsequent expeditions to the Bunger Oasis. Seismological research will allow to better understand the structure of the Earth’s interior, in particularolarity of its nucleus. In turn, geomagnetic monitoring, conducted near the Earth’s south magnetic pole, will provide a better understanding of the dynamics of the processoArctowski and the Arctowski station, the seismic research will allow to better understand the structure of the Earth’s interior, in particular.
The station may also be a testing ground for automatic measurement equipment and other devices designed for space missions. According to the originator and implementer of the revitalization program, Professor Mark Lewandowski of the IGF of the Polish Academy of Sciences, Bunger’s Oasis is a perfect terrestrial analogue of the surface of Mars.
– There is a field here for co-ohe cooperation with the Polish space industry and industrial partners in the design, manufacture and application of high-performance sources ofoenergy sources, as well as data transmission via satellite – he said, quoted in a communiqué published on PAN’s website, prof. Lewandowski. – In the future, plans can be made to erect a modern survival capsule, in which theowhere a crew of several people could spend several months in an oasis conducting scientific research,” he added.
Sourceosource: Polish Academy of Sciences, photo. TobbeTardigrade/ Wikimedia Commons/ CC BY-SA 4.0. The photo shows the western part of the station. Photo from 2016.